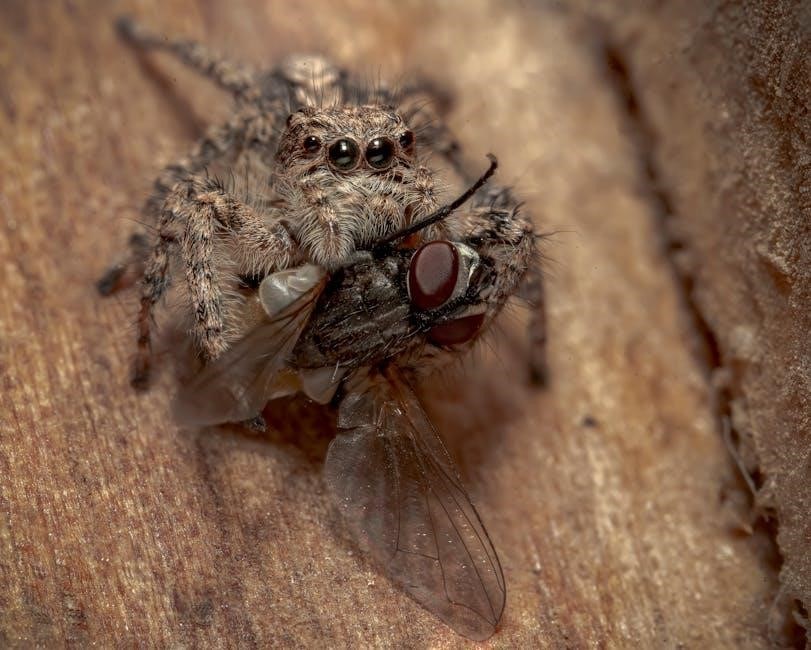
Jumping spiders are agile predators requiring a balanced diet of live insects, fruits, and nectar. Their feeding needs vary by age, size, and moult stages, making proper nutrition essential for health. Overfeeding or incorrect prey size can lead to health issues, while supplementary treats like fruits provide additional nutrients. Understanding their feeding behavior and environment ensures a thriving pet spider.
Understanding the Importance of Proper Nutrition
Proper nutrition is vital for jumping spiders, as it directly impacts their growth, energy, and overall health. A well-balanced diet ensures they develop strong physical traits and vibrant coloration. Overfeeding or underfeeding can lead to health issues, such as obesity or malnutrition. Providing the right prey size and variety prevents stress and digestive problems. Nutrition also plays a role in their behavior and hunting abilities, making it crucial to tailor their diet to their age, size, and life stage for optimal well-being.
Overview of Jumping Spider Dietary Needs
Jumping spiders primarily feed on live insects like crickets, flies, and roaches, which provide essential proteins. They also enjoy occasional treats such as fruits and nectar for added nutrients. The diet should include a variety of prey to ensure a broad spectrum of vitamins and minerals. Feeding techniques like using tweezers or brushes can help immobilize prey, making meals easier for the spider. A balanced diet supports their energy, growth, and vibrant coloration, ensuring they remain active and healthy.
Types of Food for Jumping Spiders
Jumping spiders primarily consume live insects like crickets, flies, and roaches. Fruits and nectar serve as occasional treats, while commercial diets offer convenience and balanced nutrition.
Live Insects as a Primary Food Source
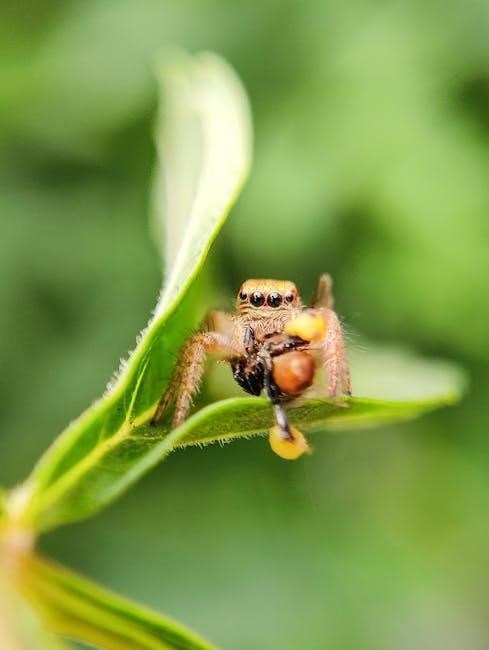
Live insects are the cornerstone of a jumping spider’s diet, providing essential nutrients for growth and energy. Crickets, flies, and roaches are popular choices, offering a balanced mix of proteins and fats. Mealworms can also be included, though wax worms should be given sparingly due to their high fat content. Insects should be gut-loaded and dusted with calcium for added nutrition. Slowing prey with a brush or brief refrigeration ensures easier feeding, promoting a stress-free meal for the spider.
Fruits and Nectar as Supplementary Treats
Fruits like strawberries, watermelon, and grapes are sweet treats for jumping spiders, offering a natural source of sugar. Nectar from these fruits provides energy and variety in their diet. These treats should be offered occasionally to supplement live prey, aiding in hydration and nutrient intake. However, fruits should never replace primary protein sources, as live insects remain essential for their overall health and vitality. This balanced approach ensures a happy and thriving pet spider.
Commercial Diets and Their Role in Feeding
Commercial diets, such as mealworms and wax worms, are convenient and nutritious options for feeding jumping spiders. These diets are often pre-packaged and easy to store, providing a consistent food source. They are particularly useful for breeders or keepers who prefer a reliable alternative to live insects. However, they should not fully replace live prey, as variety is key to a spider’s health. Commercial diets can be a valuable addition to a balanced and varied feeding routine for your pet jumping spider.

Feeding Techniques for Jumping Spiders
Feeding jumping spiders involves using tweezers, immobilizing prey with a brush, or offering live insects in an enclosed space to ensure successful and stress-free meals for your pet.
Using Tweezers for Feeding
Using tweezers is an effective method for feeding jumping spiders, allowing precise control over offering prey. Gently hold live insects with the tweezers, ensuring the spider can see and approach the food. However, if the prey moves too much, the spider may hesitate. To solve this, immobilize the insect with a paint brush or chill it slightly in the refrigerator beforehand. This technique makes feeding stress-free and ensures your spider enjoys its meal efficiently.
Immobilizing Prey with a Paint Brush
When feeding live prey, immobilizing it with a soft-bristled paint brush can help reduce stress for the spider. Gently press the brush against the insect to restrict its movement without causing harm. This method allows the jumping spider to approach confidently, ensuring a successful feeding session. It’s especially useful for skittish spiders or overly active prey, making mealtime more efficient and enjoyable for both you and your pet.
Feeding Live Prey in an Enclosed Environment
Feeding live prey within an enclosed environment ensures the spider can hunt naturally without distractions. Place the prey in a secure, escape-proof container to prevent escape attempts. This method mimics the spider’s natural hunting behavior, reducing stress and promoting a successful feeding experience. Ensure the enclosure is well-ventilated and free from hazards, allowing the spider to thrive in a controlled yet stimulating setting.

Feeding Schedule and Frequency
Feed jumping spiders every 2-3 days for adults and more frequently for spiderlings. Adjust based on size, age, and post-moult stages to ensure optimal health and energy levels.
How Often to Feed Based on Spider Size and Age
Feeding frequency for jumping spiders varies with size and age. Spiderlings require daily feeding due to rapid growth, while juveniles can be fed every 2-3 days. Adults, especially larger species, need food every 3-4 days. Adjustments may be needed during moulting stages, as spiders often stop eating. Overfeeding can lead to health issues, so observe your spider’s behavior and body condition to determine the best feeding schedule.
Signs Your Spider is Hungry or Full
A hungry jumping spider may exhibit active behavior, such as approaching the enclosure walls or vibrating webs, indicating it’s ready to eat. A taut abdomen suggests hunger, while a distended one signals fullness. If your spider ignores prey or shows lethargy, it’s likely sated. Observing these cues helps avoid overfeeding and ensures a balanced diet tailored to its needs.
Adjusting Feeding Frequency Seasonally
Jumping spiders’ feeding needs vary with seasonal changes. During warmer months, they are more active and may require more frequent feeding, while in cooler periods, their metabolism slows, reducing hunger. Offer food every 2-3 days in spring and summer, and less often in fall and winter. Observe your spider’s behavior and abdomen size to determine if adjustments are needed, ensuring you meet their seasonal nutritional demands without overfeeding.
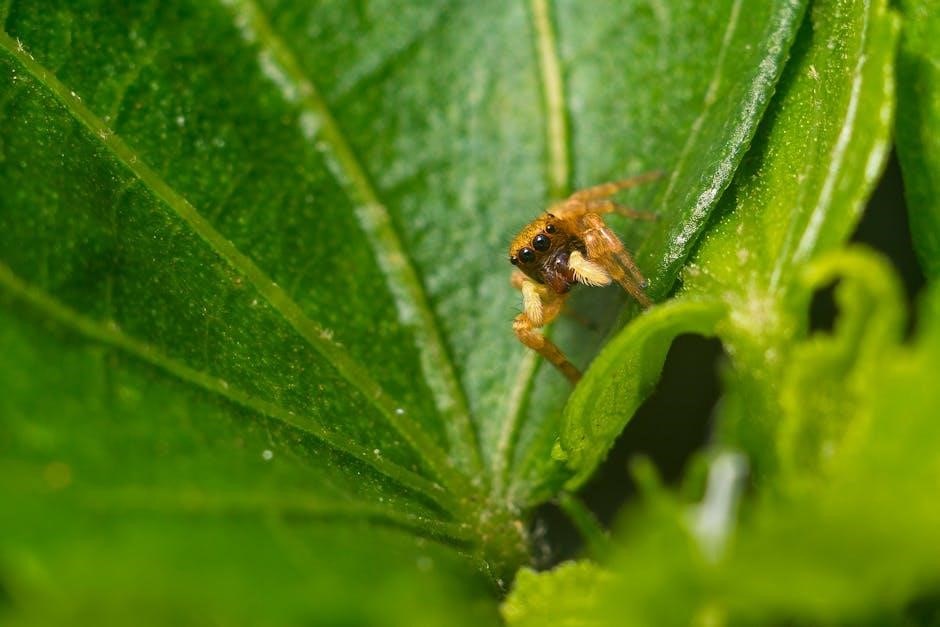

Prey Size and Selection
Proper prey size is crucial for jumping spiders, ensuring safe and effective feeding. Select insects that match the spider’s size, avoiding prey larger than 1.5 times their body size to prevent harm and promote healthy digestion. A varied diet enhances nutrient intake and overall well-being, making prey selection a key aspect of their care.
Choosing Prey Appropriate for Spider Size
Selecting prey that matches your jumping spider’s size is vital for safe and effective feeding. Spiderlings thrive on small insects like fruit flies, while larger spiders can handle crickets or roaches. Ensure prey is proportional to the spider’s body size, avoiding items too big or small. For example, a spiderling might eat a small fruit fly, while an adult could manage a cricket or mealworm. Proper size selection prevents harm and ensures the spider can digest its food efficiently.
Ensuring Prey is Not Larger Than 1.5 Times the Spider
Feeding prey larger than 1.5 times the spider’s size can lead to digestion issues or stress. Stick to this guideline to ensure the spider can consume and process the meal effectively. For example, a spiderling might eat a small fruit fly, while an adult could handle a cricket or mealworm. Proper size selection promotes healthy digestion and prevents potential complications, ensuring your pet spider thrives without unnecessary strain.
Variety in Prey to Promote Health
Offering a diverse range of prey ensures your jumping spider receives a broad spectrum of nutrients. Rotate between crickets, flies, roaches, and occasional wax worms to prevent dietary boredom and deficiencies. Varying prey sizes and types mimics their natural hunting behavior, keeping them stimulated and healthy. Avoid relying solely on one food source, as this can lead to nutritional imbalances over time. A varied diet supports optimal growth, energy, and overall well-being for your pet spider.

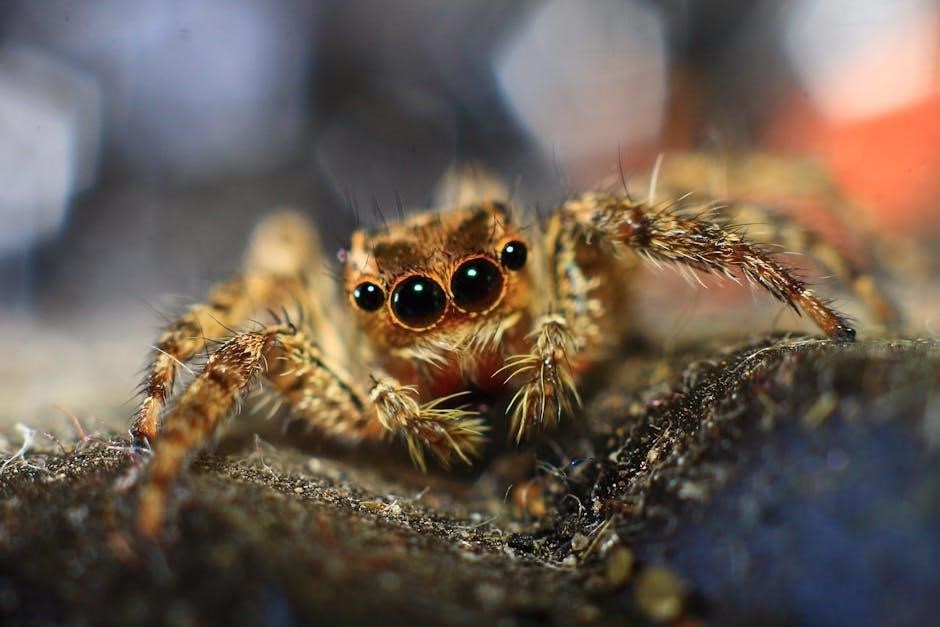
Feeding Live Prey
Live insects like crickets, flies, and roaches are essential for jumping spiders, providing natural hunting stimulation. Tweezers or brushes can help immobilize prey, making feeding easier and safer.
Preparing Live Insects for Feeding
Live insects should be stored in a well-ventilated container with food and water to keep them healthy. Before feeding, ensure prey is appropriately sized for your jumping spider. Gently clean the insects and remove any uneaten food. To slow down active prey like flies or crickets, briefly place them in the refrigerator for a few minutes. This makes feeding easier and reduces stress on the spider. Always handle insects carefully to avoid harming them.
Slowing Down Prey for Easier Feeding
To make feeding easier, place live prey like flies or crickets in the refrigerator for a few minutes before offering them to your spider. This slows their movement without harming them. Alternatively, gently pat the insect with a soft brush to calm it. Ensure the prey is appropriately sized and healthy to prevent stressing your spider. This method helps your pet focus on feeding without being overwhelmed by hyperactive prey.
Observing Spider Behavior During Feeding
Observe your jumping spider’s behavior during feeding to ensure a successful meal. Watch for signs of hunger, such as rapid movements toward prey. If the spider hesitates or shows no interest, it may already be full. Note if it stops eating or begins web-spinning, indicating satiation. If prey remains uneaten, remove it to avoid stressing your spider. This observation helps tailor feeding schedules and prey selection, promoting a healthy and stress-free environment for your pet.

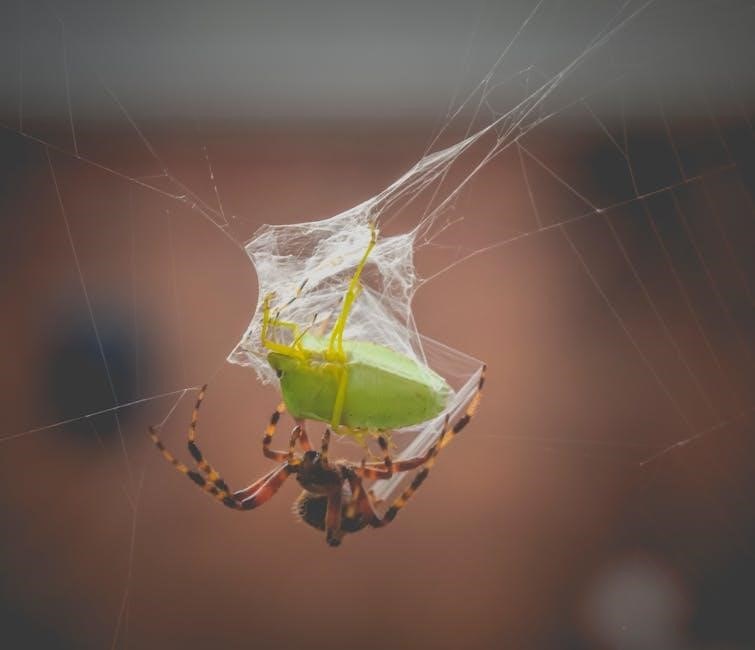
Common Feeding Mistakes to Avoid
Common feeding mistakes include overfeeding, offering prey too large, and feeding wild insects. These errors can harm your spider’s health, so awareness is key. Always provide appropriately sized prey and avoid wild insects to prevent potential risks. Monitoring your spider’s behavior and adjusting feeding schedules can help prevent these issues, ensuring a healthy and thriving pet spider. Avoid these pitfalls to maintain optimal care for your jumping spider.
Overfeeding and Its Health Consequences
Overfeeding jumping spiders can lead to obesity and related health issues, such as poor digestion and reduced mobility. It can also shorten their lifespan by putting strain on their internal systems. Recognizing signs like an unusually round abdomen or lethargic behavior is crucial. Avoid feeding more than necessary, as spiders have small stomachs and thrive on moderate meals. Ensuring portion control and maintaining a balanced feeding schedule prevents overfeeding, promoting a long and healthy life for your pet spider.
Feeding Wild Insects and Potential Risks
Feeding wild insects to jumping spiders poses risks, as they may carry pesticides, parasites, or diseases. These contaminants can harm the spider, leading to illness or death; Wild insects may also be larger or unsuitable for the spider’s size, causing feeding issues. It’s safer to use captive-bred insects, ensuring they are free from harmful substances and appropriately sized for the spider’s needs. This practice helps maintain the spider’s health and avoids potential threats from wild prey.
Ignoring Spider Moulting Stages in Feeding
Ignoring a jumping spider’s moulting stages can lead to feeding issues. During moulting, spiders stop eating as they shed their skin, and forcing food can cause stress or regurgitation. Recognizing moulting signs, such as reduced activity or a swollen abdomen, is crucial. Avoid feeding until the spider resumes normal behavior, ensuring its digestive system is ready. Mistiming meals during moulting can harm the spider’s health and disrupt its growth cycle, emphasizing the importance of observing and respecting this natural process.

Feeding Baby Jumping Spiders
Baby jumping spiders require smaller, nutrient-rich prey like fruit flies. Feed them frequently, 2-3 times daily, ensuring prey size matches their mouth size for optimal growth and health.
Special Dietary Needs for Spiderlings
Spiderlings require live prey like small fruit flies or pinhead crickets, ensuring prey is proportional to their size. Feed daily, as they grow rapidly. Avoid large insects, which can harm them. Provide a varied diet to promote healthy development, and consider offering nectar as an occasional treat for added nutrition and energy. Proper hydration and a clean environment are also crucial for their survival and growth.
Feeding Frequency for Young Spiders
Spiderlings require daily feeding with small, live prey like fruit flies or pinhead crickets. As they grow, gradually increase the interval to every other day. Overfeeding can harm young spiders, so monitor their size and activity. Provide prey proportional to their body size and observe their behavior to adjust the schedule. Offering nectar as a supplementary treat can also support their growth without overfeeding, ensuring a balanced and nutritious diet for healthy development.
Recommended Prey for Baby Spiders
Baby jumping spiders thrive on tiny prey such as fruit flies and pinhead crickets. These insects are small enough for their mouthparts and provide essential nutrients. Fresh fruit flies from a culture are ideal, as they are less likely to cause harm. Avoid using prey larger than the spider’s body to prevent injury. This balanced diet supports healthy growth and development, ensuring your young spider remains robust and active. Offering live prey daily meets their high energy needs during the growth stage.
Feeding Adult Jumping Spiders
Adult jumping spiders thrive on a diverse diet of live insects like crickets, flies, and roaches. Supplementary treats such as fruit nectar can be occasionally offered. They don’t need to eat daily, making their feeding schedule flexible and dependent on their activity levels and environment.
Dietary Requirements for Adult Spiders
Adult jumping spiders require a balanced diet rich in protein, primarily obtained from live insects. Crickets, flies, and small roaches are ideal, offering essential nutrients for vitality and growth. Supplementary treats like fruit nectar provide sugars, serving as occasional energy boosts but should not replace main meals. A varied diet prevents nutritional deficiencies, ensuring overall health and maintaining their vibrant coloration and active behavior. Avoid overfeeding to prevent health issues such as obesity, which can hinder their agility and lifespan. Regular feeding with suitable prey ensures optimal well-being and satisfaction of their dietary needs.
Feeding Frequency for Adults
Adult jumping spiders should be fed every 2-3 days, as they have a moderate metabolism. The frequency may vary based on the spider’s size and activity level. Overfeeding can lead to health issues, so it’s important to observe your spider’s behavior and body condition. If the spider appears full or lethargic, skip a feeding cycle. Proper scheduling ensures they remain active and healthy, avoiding potential weight-related problems that could affect their agility and lifespan. Always monitor their response to feeding to adjust the schedule accordingly.
Supplementary Treats for Adults
Adult jumping spiders can occasionally be treated with small amounts of fruit or nectar, such as watermelon, strawberries, or mangoes. These sugary treats provide energy and variety, enhancing their diet. However, they should not replace live insects, as the latter are essential for protein. Offer fruits sparingly to avoid overfeeding and ensure the spider remains active and healthy. This approach keeps them stimulated and satisfied, promoting overall well-being without disrupting their natural feeding instincts or dietary balance.
Feeding Tools and Gadgets
Feeding tools like tweezers and paint brushes help immobilize or offer prey to jumping spiders. These gadgets make feeding easier and more efficient for both spider and owner.
Using Feeding Tweezers Effectively
Feeding tweezers are essential for offering live prey to jumping spiders. They allow precise control, making it easier to present food without startling the spider. Gently hold the prey, ensuring it remains still and within the spider’s reach. This method is particularly useful for skittish or young spiders. Tweezers also help prevent prey from escaping, reducing stress for both the spider and owner. Regular cleaning of the tweezers is crucial to maintain hygiene and prevent the spread of disease.
Feeding Brushes and Their Benefits
Feeding brushes are a valuable tool for managing live prey during feeding sessions. They allow you to gently guide or immobilize insects, making it easier for your jumping spider to approach and capture its food. This method minimizes stress for both the spider and the prey, ensuring a calm and effective feeding process. Brushes are particularly useful for delicate or skittish spiders, promoting a natural hunting experience while maintaining control over the feeding environment.
Other Innovative Feeding Tools
Beyond tweezers and brushes, innovative feeding tools enhance the efficiency and safety of feeding jumping spiders. Magnetic feeding dishes with movable parts allow prey to move naturally, stimulating the spider’s hunting instinct. Automated feeders dispense food at set intervals, ensuring consistency. Suction cup holders secure live insects, preventing escape. These tools cater to different spider personalities and keeper preferences, optimizing feeding sessions while reducing stress on both the spider and the prey.

FAQs: Jumping Spider Feeding Guide

Common questions include how often to feed, prey size limits, and suitable treats. Answers address feeding frequency, prey selection, and signs of hunger or fullness in spiders.
How Do I Know If My Spider is Hungry?
Determining if your jumping spider is hungry involves observing its behavior and physical cues. Hungry spiders often exhibit increased activity, approaching the enclosure walls or showing interest in movement. They may also vibrate their webs or display hunting postures. A hungry spider might appear more alert or active compared to its usual demeanor. Additionally, spiders that have not eaten recently may have a slimmer abdomen or show eagerness when prey is introduced. These signs indicate it’s time to feed.
Can Jumping Spiders Eat Human Food?
Jumping spiders primarily consume live insects, but they can occasionally eat human food like fruit nectar or sugary substances. Fruits such as watermelon, strawberries, and mangoes provide a sweet treat and essential nutrients. However, human food should only be offered as an occasional supplement and not as a replacement for their main diet of insects. Over-reliance on human food can lead to nutritional imbalances, so it’s crucial to maintain a balanced diet focused on live prey.
How Long Can a Jumping Spider Go Without Food?
Jumping spiders can survive several weeks without food, depending on their age, size, and overall health. Adult spiders generally tolerate fasting longer than juveniles, which require more frequent feeding due to rapid growth. However, prolonged fasting can lead to stress and health issues. It’s important to maintain a regular feeding schedule to ensure optimal health and energy levels for your pet jumping spider.
Proper nutrition and feeding techniques are vital for a jumping spider’s health. By understanding their needs and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure a happy, thriving pet spider.
Best Practices for Feeding Jumping Spiders
Feed live insects like crickets, mealworms, and flies, ensuring prey size is appropriate for the spider’s age and size. Use tweezers or brushes to immobilize prey, promoting stress-free feeding. Offer supplementary treats like fruits or nectar in moderation. Maintain a feeding schedule based on the spider’s stage and activity level, avoiding overfeeding. Observe your spider’s behavior to adjust feeding frequency and prey variety, ensuring a balanced diet for optimal health and longevity.
Ensuring a Happy and Healthy Pet Spider
Provide a stimulating environment with adequate space and visual cues to encourage natural hunting behavior. Maintain proper temperature and humidity levels to support your spider’s health. Offer a varied diet, including live insects and occasional treats like fruits or nectar, to ensure nutritional balance. Regularly observe your spider’s behavior and physical condition to detect any signs of stress or illness. A clean, well-maintained enclosure and consistent care routine will help keep your jumping spider thriving and content.



